Energy Automation (SCADA)
Automation for Powerful and Smart Power Grids
Power automation, measurement, protection, monitoring, billing and automation, control and control of other electrical systems for low voltage electrical networks in buildings are managed by SCADA systems. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is a critical technology for monitoring and managing power grids through a central platform. These systems increase energy efficiency while at the same time ensuring grid security.
SCADA Systems: Automation for Powerful and Smart Power Grids
Power automation, measurement, protection, monitoring, billing and automation, control and control of other electrical systems for low voltage electrical networks in buildings are managed by SCADA systems. SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) is a critical technology for monitoring and managing power grids through a central platform. These systems increase energy efficiency while at the same time ensuring grid security.
Tackling the Power Grid Challenges of the Near Future
Megatrends such as digitalization, decarbonization and distributed power generation are rapidly taking hold in the global energy market. To adapt to these changes and meet the growing demand for energy, electrical networks must digitize and become smarter using IoT (Internet of Things) technologies. SCADA systems are the cornerstones of this digital transformation and are evolving to make electrical networks more efficient, flexible, and sustainable.
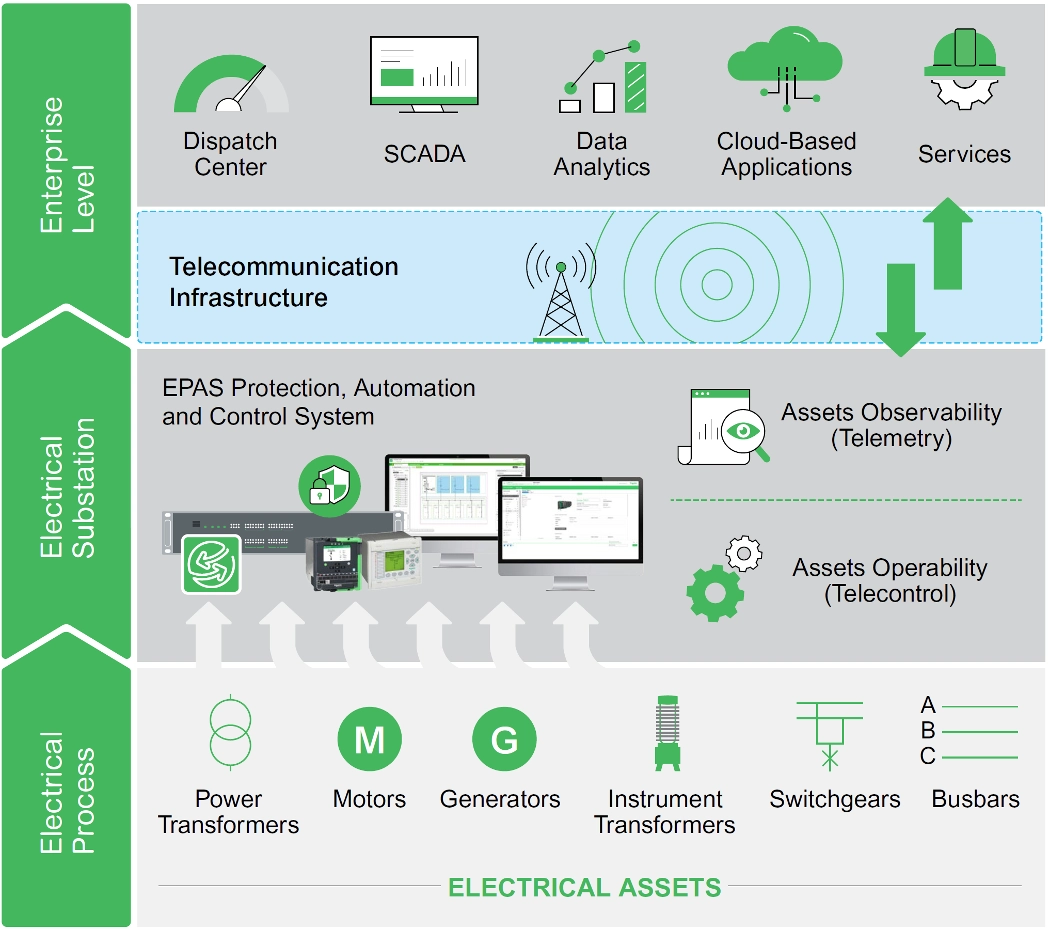
Smart Grid Transformation and Power Management with SCADA
It plays a crucial role in the digitalization of grids. Schenider's EcoStruxure™ Power Automation System (EPAS) revolutionizes power management with SCADA technology. It enhances data security, safety, and operational efficiency throughout the design, construction, operation, and maintenance processes. EPAS provides real-time monitoring and control at every stage of the grid, ensuring safer and more efficient system operation.
The Future Role of SCADA in Smart Grids
These are the core technologies supporting the smart grid transformation. These systems optimize energy management, increase efficiency, and monitor energy consumption. They also enable rapid detection of grid faults and automated corrective action. SCADA accelerates the digital transformation of electrical grids, providing safer, more efficient, and more sustainable energy solutions.
Endüstriyel ve altyapı sistemlerinin izlenmesi ve kontrol edilmesi için kullanılan bir sistemdir. Bu sistem, elektrik şebekeleri, su arıtma tesisleri, otomasyon hatları gibi birçok alanda veri toplar, izler ve kontrol eder. SCADA, operasyonel verimliliği artırmak, arızaları tespit etmek ve sistemleri optimize etmek için kullanılır.
Enerji yönetimi, su ve atık su arıtma, ulaşım, gaz ve petrol endüstrileri, otomasyon hatları ve bina yönetim sistemleri gibi birçok endüstriyel alanda kullanılır. Elektrik şebekeleri, su arıtma tesisleri ve HVAC sistemleri gibi altyapıların izlenmesi ve kontrol edilmesinde özellikle yaygındır.
Gerçek zamanlı izleme: Sistemlerin durumu anında izlenebilir, bu da hızlı müdahaleyi mümkün kılar.
Verimlilik artışı: Otomatikleştirilmiş kontrol, manuel müdahale ihtiyacını azaltır ve verimliliği artırır.
Arıza tespiti: Sistem arızaları daha hızlı tespit edilip, müdahale edilebilir.
Uzaktan erişim: Kullanıcılar, uzaktan erişimle sistemleri kontrol edebilir.
Veri toplama ve raporlama: Operasyonel veriler toplanarak analiz edilebilir, uzun vadeli stratejiler geliştirilebilir.
Sistemi, sensörler, kontrollü cihazlar, haberleşme altyapıları ve yazılım platformlarından oluşur. Sensörler, saha cihazlarından verileri toplar, bu veriler merkezi bir kontrol birimine iletilir. Kontrol birimi, verileri işler, analiz eder ve kararlar alır. Ayrıca, kullanıcılar uzaktan erişim ile sisteme müdahale edebilir. Bu süreç, sistemlerin sürekli izlenmesi ve kontrol edilmesine olanak tanır.
Güçlü siber güvenlik önlemleri ile korunur. Bu önlemler arasında güvenli iletişim protokolleri, şifreleme, erişim kontrol sistemleri, çok faktörlü kimlik doğrulama ve düzenli yazılım güncellemeleri bulunur. Ayrıca, ağ tabanlı SCADA sistemleri, güvenlik duvarları ve izleme araçları ile korunarak dış tehditlerden izole edilir.
SCADA sistemleri, sıcaklık, basınç, akış, nem, enerji tüketimi, voltaj, akım gibi sensör verilerini toplar. Bu veriler, elektrik şebekelerindeki yük durumunu izlemek, su ve gaz hatlarındaki akışı kontrol etmek ve HVAC sistemlerinin verimli çalışmasını sağlamak gibi işlemler için kullanılır.